What Is data analytics in laboratory medicine?
Data analytics in laboratory medicine is the process of extracting meaningful insights from data to support evidence-based decision-making. It involves:
- Using real-world laboratory data to uncover trends and patterns
- Applying visualization techniques to make complex data understandable
- Conducting exploratory and statistical analyses to identify relationships
- Using machine learning and advanced algorithms for predictive insights
- Communicating results clearly to drive informed clinical and operational actions
The data analytics lifecycle
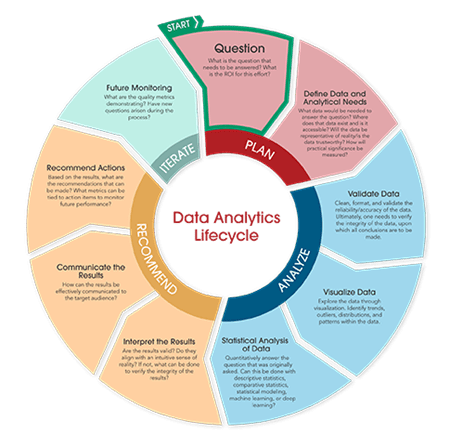
Laboratory data analytics is transforming healthcare by turning complex datasets into actionable insights that improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency. At the heart of this transformation is the Data Analytics Lifecycle, a structured framework widely used in data science to ensure accuracy, reliability, and impact.
1. Define the question
Every successful analytics project starts with a clear question. What problem are we solving? What is the ROI for this effort? In laboratory data analytics, defining the right question ensures meaningful results.
2. Identify data and analytical needs
Determine what data is required and whether it is available, accessible, and statistically significant. This step is critical for data science in laboratory medicine, where data integrity drives clinical decisions.
3. Validate data quality
Clean, format, and validate data to ensure accuracy and reliability. High-quality data is the foundation of effective laboratory data analytics and predictive modeling.
4. Visualize data
Use data visualization techniques to uncover trends, patterns, and outliers. Visualization is a key component of data science, helping laboratories interpret complex datasets quickly.
5. Perform statistical analysis
Apply advanced statistical methods and machine learning algorithms to extract insights. From comparative statistics to deep learning, this step powers predictive analytics in laboratory medicine.
6. Interpret results
Do the results align with expectations? Validate findings and assess integrity before making recommendations. In data science, interpretation ensures actionable insights.
7. Communicate insights
Share results effectively with stakeholders. Clear communication is essential for turning laboratory data analytics into real-world improvements in patient care.
8. Recommend actions
Based on the analysis, propose evidence-based actions to optimize laboratory workflows and clinical outcomes.
9. Monitor and iterate
Track quality metrics and monitor performance over time.
Why It Matters?
The Data Analytics Lifecycle enables laboratories to improve laboratory operations to improve patient care for all. By following this structured approach, laboratories can transform raw lab data into actionable insights.
Benefits for clinical decision‑making
Clinical decision support is stronger when analytics surfaces the right insight at the right time:
- Fewer diagnostic errors: Pattern recognition reduces misinterpretation, especially across multi‑analyte panels.
- Timely interventions: Outlier detection and alert routing accelerate critical value communication.
- Evidence consistency: Standardized reference ranges.
- Cross‑disciplinary collaboration: Lab, informatics, data science, and clinical teams align on shared metrics and dashboards.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What skills are needed for laboratory data analytics?
Successful laboratory data scientists combine clinical laboratory knowledge, statistical expertise, programming skills (Python, R, SQL), and understanding of healthcare data standards and regulations.
What types of data are analyzed in laboratory medicine?
Laboratory data analytics utilizes test results, quality control data, instrument performance metrics, turnaround times, specimen information, clinical diagnoses, demographics, medications, and outcomes data.
How can laboratories get started with data analytics?
Begin with well-defined problems, ensure data infrastructure and governance are in place, develop or recruit analytical talent, start with manageable projects demonstrating clear value, and scale successful initiatives.
Get involved: Training & community
- Learn more: Explore ADLM courses on data analytics in laboratory medicine.
- Join us: Attend the ADLM Data Science Symposium to learn best practices, tools, and case studies.
- Upskill: Consider taking the Data Analytics Certificate program.
- Connect: Participate in community forums on The Artery to share use cases or ask questions.
